Research projects
City Logistics
The research team has focused on several areas of city logistics. In previous projects, we have investigated brownfield areas in Budapest, the application of the Budapest tram and HÉV network to freight transport, the optimization of common loading bay systems, the development of complex cost models and various multi-stage city logistics systems. We have also been involved in the development of concepts for the improvement of Budapest’s city logistics system.
A current priority research topic is the study, modelling, and scaling of current and possible future supply chain systems for so-called urban concentrated demand point aggregations.
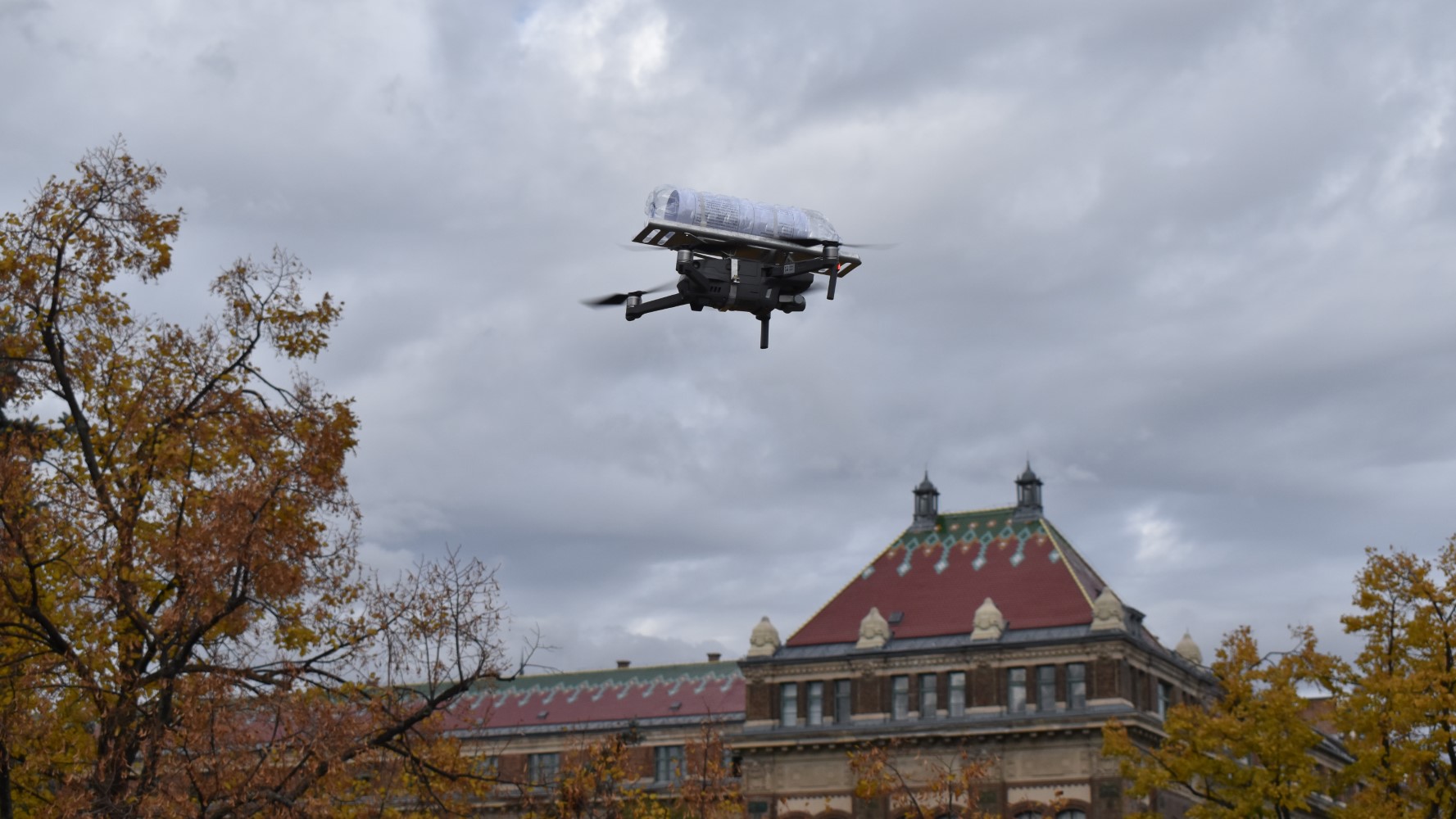
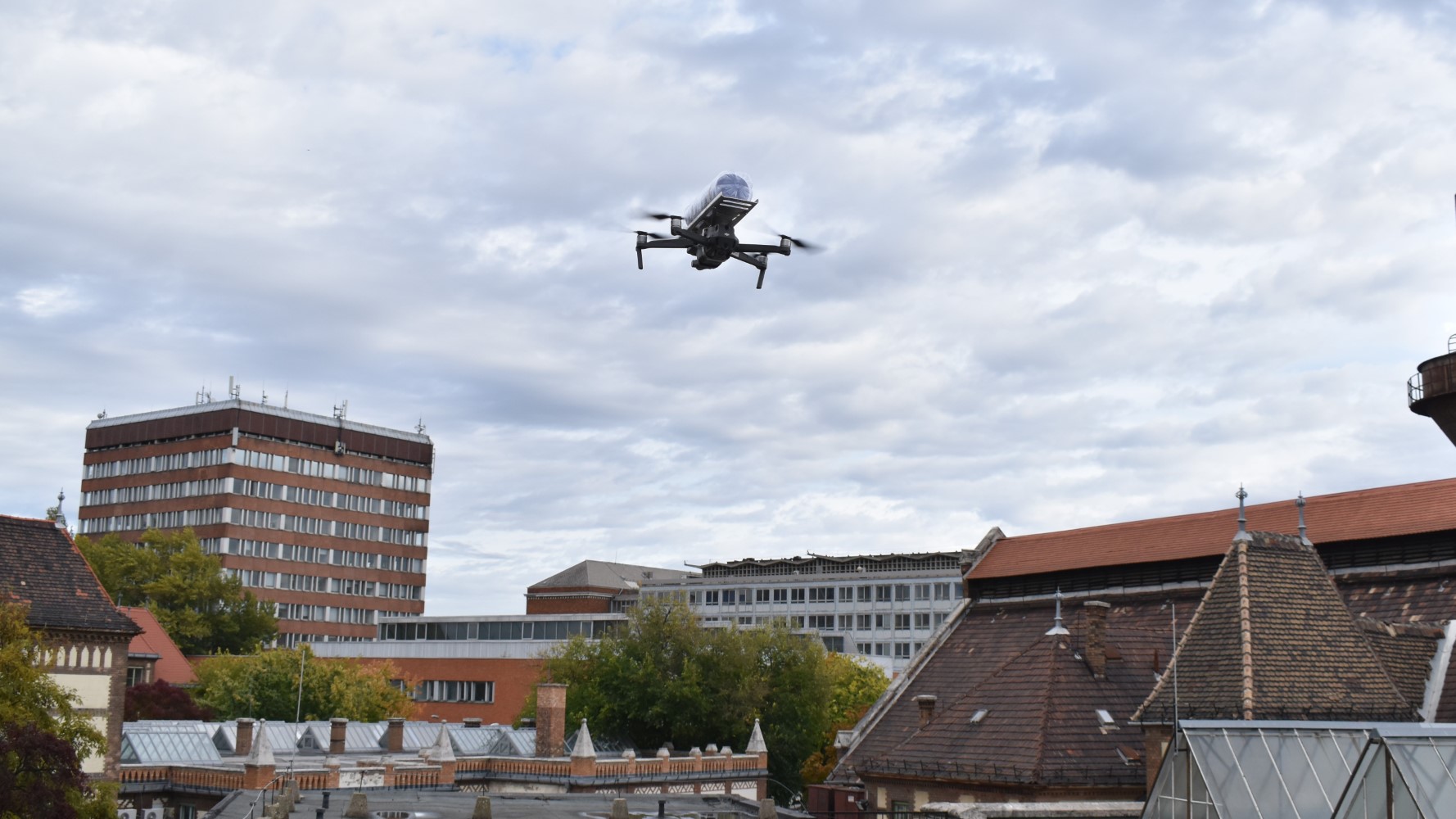
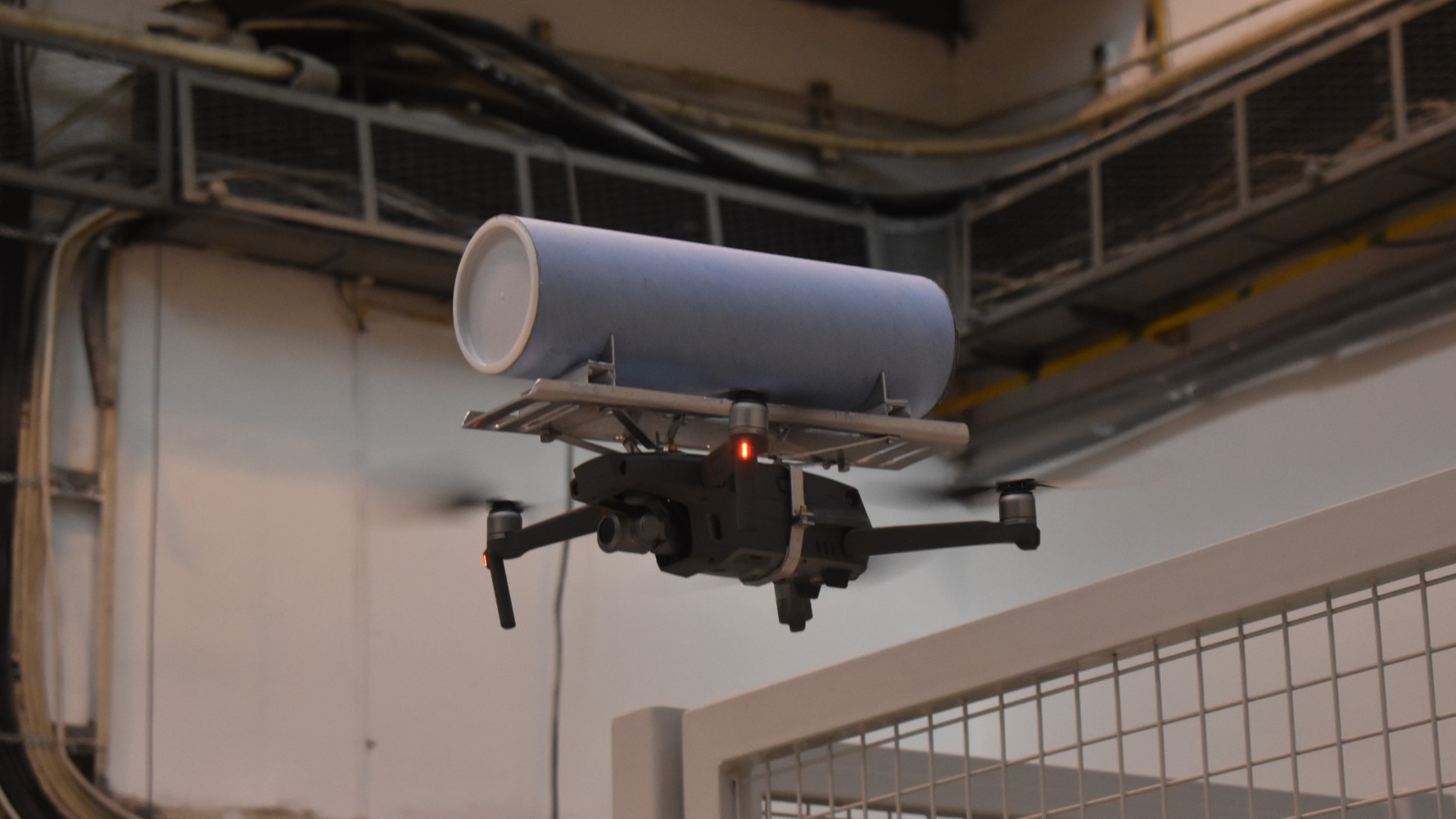






Transporting sensitive documents with drones
At the beginning of the research team’s work, we were engaged in the logistical assessment and analysis of the physical document flow at the KJK, but we were already looking at a potential future innovative solution where drones would deliver the documents.
In the next phase of the research, we have therefore tested how a drone-assisted delivery process could be physically implemented, which is currently the main focus of the research, and which raises interesting challenges such as the design of an appropriate payload.
Logistics of medical services
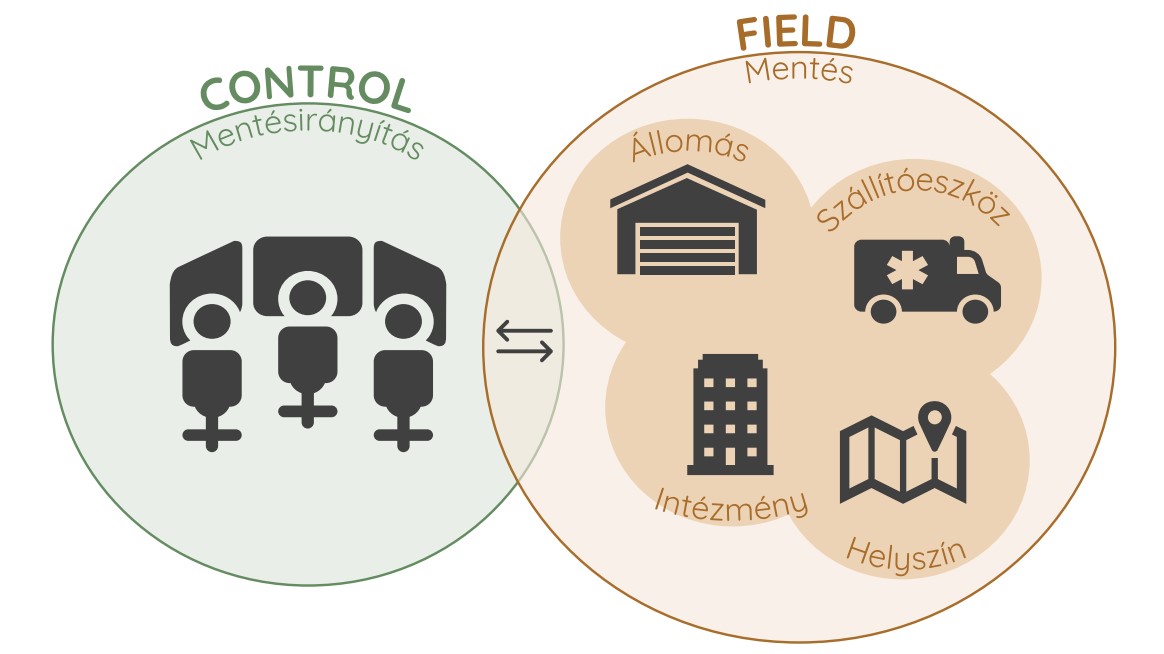
One of the most important areas of service logistics is the logistics of medical services. For several years, our research team has been working on two prominent areas of emergency patient care: rescue management and the operation of emergency departments (EDs).
What if we could plan the process of serving stochastically arriving patient care needs at an ED with the push of a button, with the appropriate time stamps? Waiting patients would also be aware of the length of the waiting time, they could track in real time when-which operation is next and what is causing the wait. All this may seem like a futuristic idea, but our research so far shows that there is great potential for improving the service processes of different EDs and integrating novel technological solutions (already proven in other areas, e.g. in production service processes) that can be applied in them.
Our goal is to quantify ED processes, to create a universal data model and, in the future, to build predictive simulation models based on digital twin technology that will be able to queue stochastically arriving requests in order to optimise lead times.
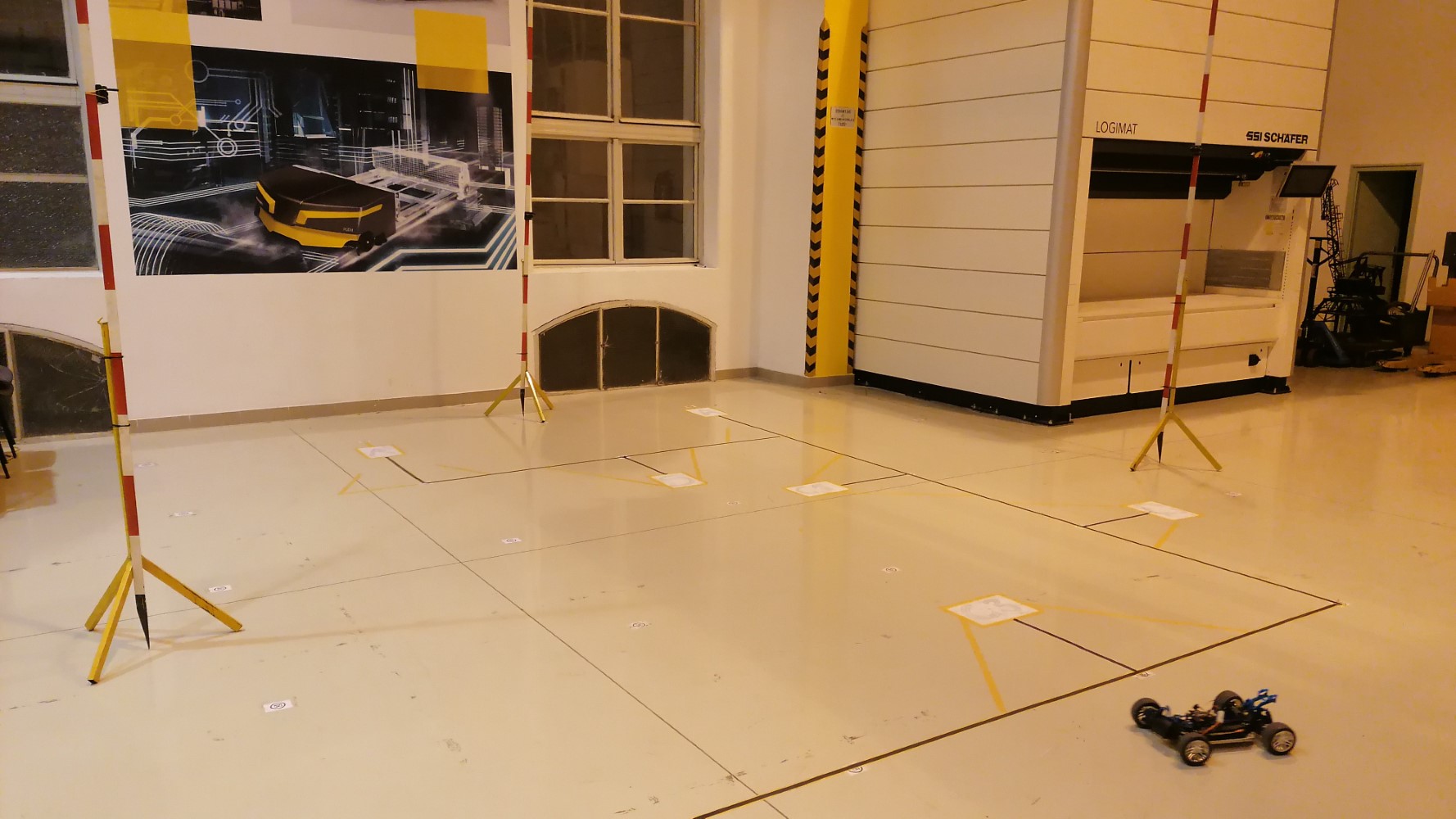


Using intelligent tools in production logistics
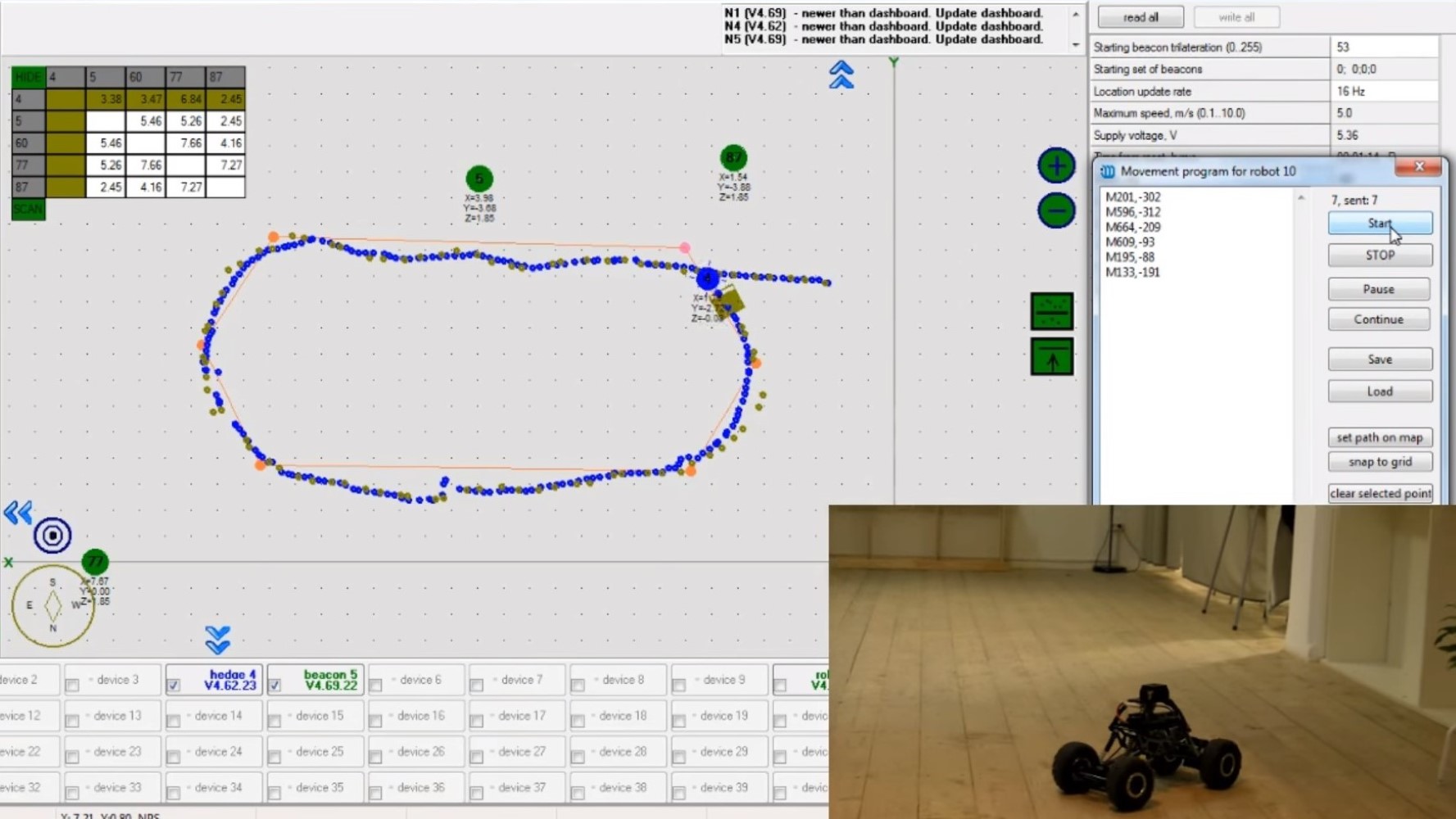
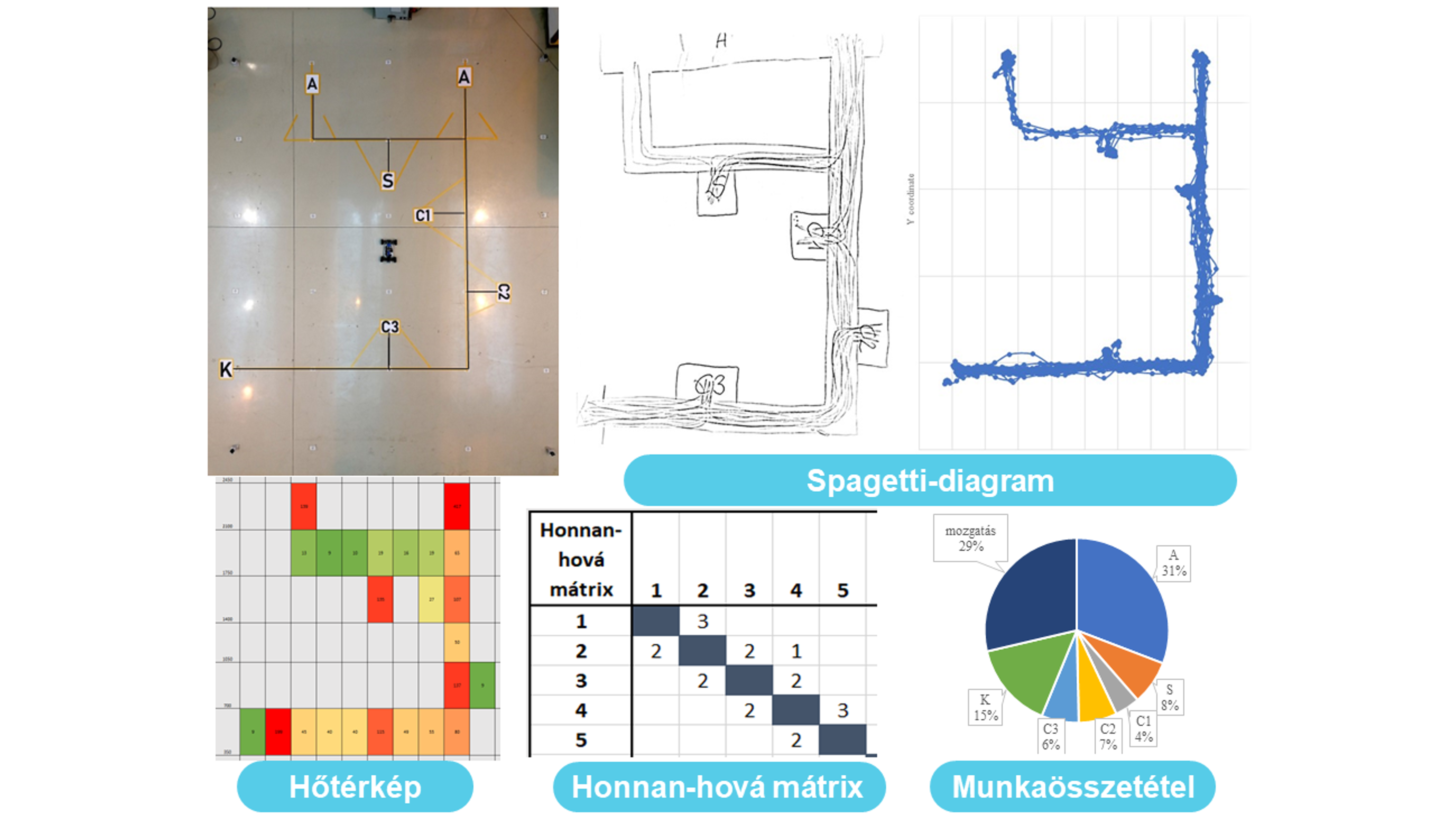
The use of indoor location systems in logistics analysis has been a major focus of the research. Time-stamped location data, which can be extracted from the observation of moving objects, is needed to map the material flow in intralogistics. Positioning systems can be used to produce digital spaghetti diagrams, heat maps, metrics and can also be used in optimisation tasks.
The research area also includes the study of the digitalisation process in manufacturing logistics companies. This will include reviewing and qualifying current best practices and developing recommendations at different depth levels of the manufacturing process using different smart tools.
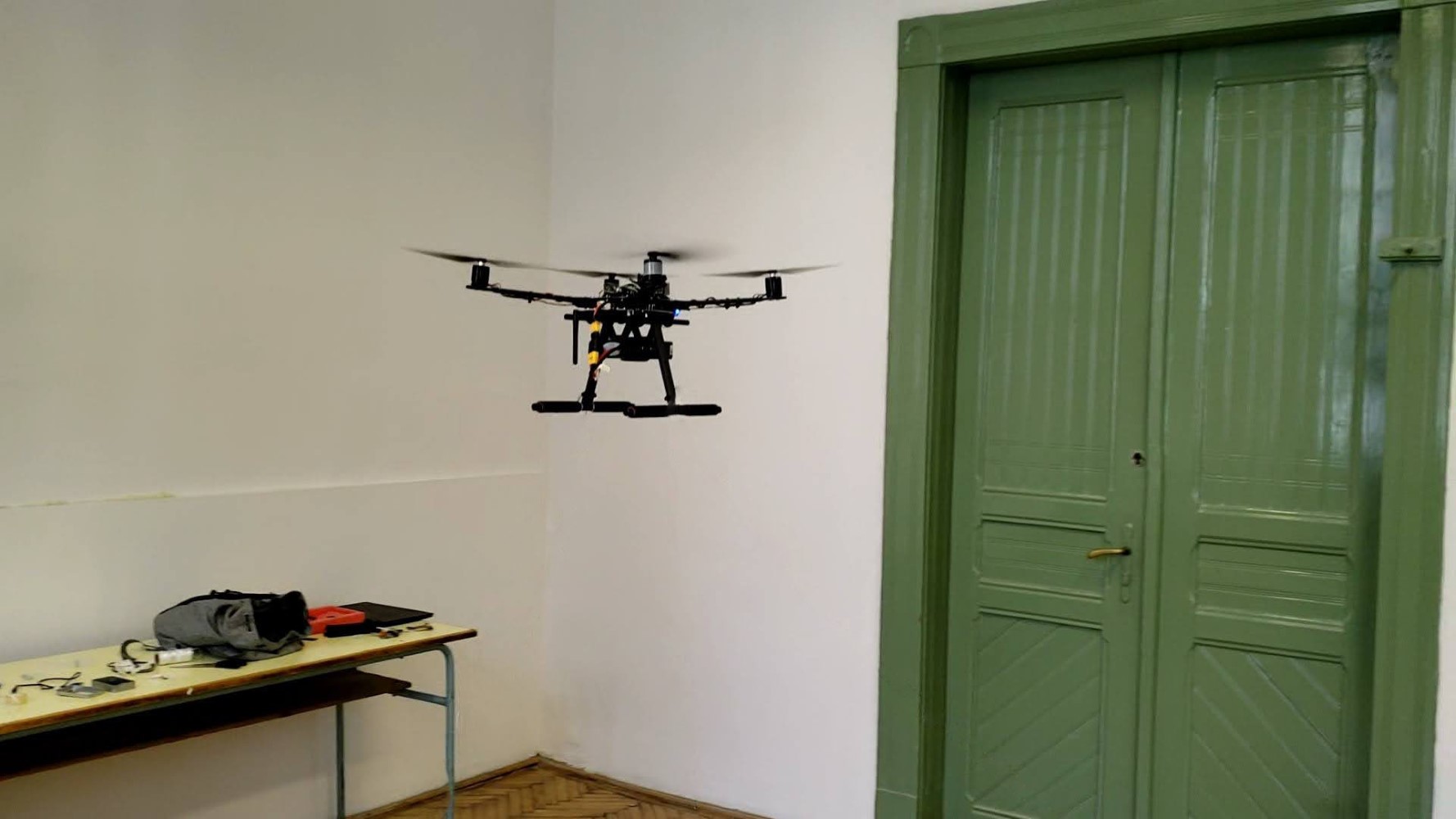
Logistics process analysis with drone-mounted moving cameras
In our previous research, we focused on the observation and analysis of movements, using motion-sensing depth sensors to investigate cycle times.
In our current research, we are working on implementing sampling workday recording, often used in industrial environments, using home-built drones. We have also complemented this research by investigating indoor positioning systems based on different technologies. Our aim is to combine these two areas, which would automate the monitoring, data processing and analysis processes that are normally very human-intensive.

Useful information
BME affiliation protocol (HU)
Rules for the uniform indication of the BME as an institution in the case of works of art and intellectual products resulting from research and development work at the BME.